reading-notes
HTML Lists, Control Flow with JS, and the CSS Box Model
Lists
- There are lots of occasions when we
need to use lists. HTML provides us with
three different types:
- Ordered lists are lists where each item in the list is numbered. For example, the list might be a set of steps for a recipe that must be performed in order, or a legal contract where each point needs to be identified by a section number.
- Unordered lists are lists that begin with a bullet point (rather than characters that indicate order).
- Definition lists are made up of a set of terms along with the definitions for each of those terms.
< ol >
The ordered list is created with
the < ol > element.
< li >
Each item in the list is placed
between an opening < li > tag
and a closing < /li > tag. (The li
stands for list item.)

*< ul >
The unordered list is created
with the < ul > element.
< li >

< dl > The definition list is created with the < dl > element and usually consists of a series of terms and their definitions. Inside the < dl > element you will usually see pairs of < dt > and < dd > elements. < dt > This is used to contain the term being defined (the definition term). < dd > This is used to contain the definition.
CSS Box Model
All HTML elements can be considered as boxes.
The CSS Box Model In CSS, the term “box model” is used when talking about design and layout.
The CSS box model is essentially a box that wraps around every HTML element. It consists of: margins, borders, padding, and the actual content. The image below illustrates the box model:
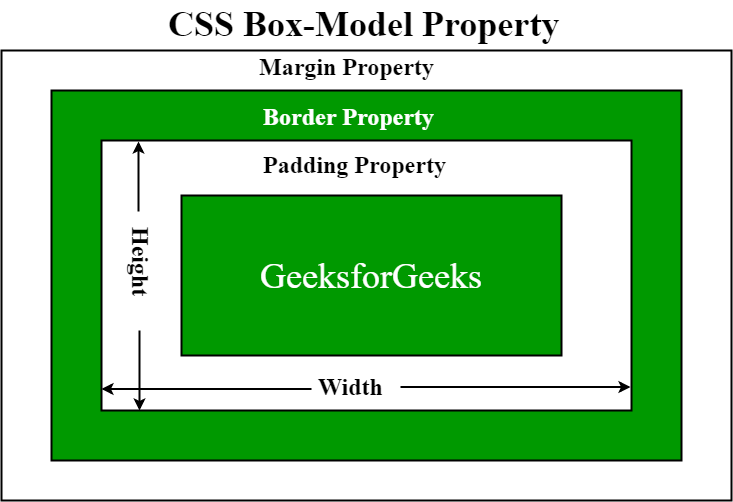
explanation of the different parts:
- Content - The content of the box, where text and images appear
- Padding - Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent
- Border - A border that goes around the padding and content
- Margin - Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent
Width and Height of an Element In order to set the width and height of an element correctly in all browsers, you need to know how the box model works.
JavaScript
JavaScript is a programming language that adds interactivity to your website. This happens in games, in the behavior of responses when buttons are pressed or with data entry on forms; with dynamic styling; with animation, etc.
- Variables Variables are containers that store values. You start by declaring a variable with the var (less recommended, dive deeper for the explanation) or the let keyword, followed by the name you give to the variable:
let myVariable;
| Variable | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| String | This is a sequence of text known as a string. To signify that the value is a string, enclose it in single quote marks. | let myVariable = ‘Bob’; |
| Number | This is a number. Numbers don’t have quotes around them. | let myVariable = 10; |
| Boolean | This is a True/False value. The words true and false are special keywords that don’t need quote marks. | let myVariable = true; |
| Array | This is a structure that allows you to store multiple values in a single reference. | let myVariable = [1,’Bob’,’Steve’,10]; Refer to each member of the array like this: myVariable[0], myVariable[1], etc. |
| Object | This can be anything. Everything in JavaScript is an object and can be stored in a variable. Keep this in mind as you learn. | let myVariable = document.querySelector(‘h1’); |
| All of the above examples too. |